Main Types of Lifting Conveyors and Their Application Characteristics
Lifting conveyors, also known as vertical conveyors or elevators, are crucial equipment in material handling systems, used to lift and lower materials vertically or nearly vertically between different heights. They solve the critical “height difference” problem in scenarios such as production lines, warehouses, and sorting centers, serving as a core component in achieving automated and continuous production logistics.
I. Main Types of Lifting Conveyors and Their Application Characteristics
Based on their working principles and structures, lifting conveyors are mainly divided into the following categories, each with its specific application focus:
1. Bucket Elevators
· Working Principle: Material is scooped up from the bottom by buckets fixed to traction components (like belts or chains), lifted to the top, and then discharged via gravity or centrifugal force.
· Suitable Materials: Bulk materials such as powders, granules, and small lumps, e.g., grain, cement, fertilizer, coal, ore, feed.
Typical Applications:
· Grain processing: Lifting raw grain to cleaning equipment, storage silos, or the top of processing equipment.
· Cement production: Lifting raw meal, clinker, finished cement.
· Chemical industry: Transporting plastic pellets, fertilizer, etc.
· Mining and metallurgy: Lifting coal, ore, slag, etc.
· Advantages: Good sealing, prevents dust leakage; high lifting height (up to tens of meters); high conveying efficiency.
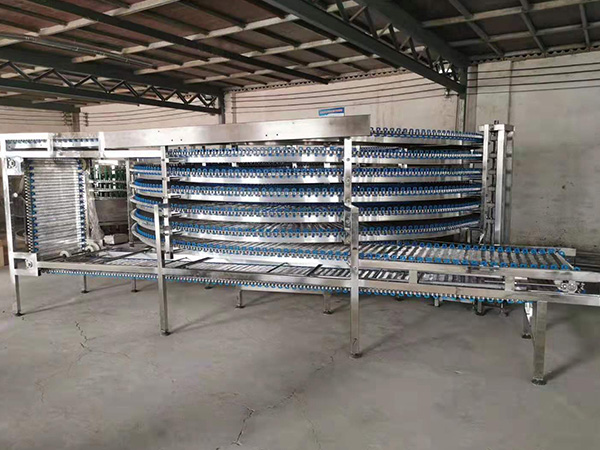
2. Z-Type / C-Type Elevators (Clamping Type / Tray Elevators)
· Working Principle: Goods are clamped or carried by flights, trays, or belts fixed to chains, moving within vertical tracks for lifting and lowering. The goods maintain a stable posture throughout the process.
· Suitable Materials: Various formed unit loads such as boxes, bags, bottles, cans, cartons, and pallets.
· Beverage and beer industry: Transporting full beverage cases, glass/plastic bottles between floors.
· Food industry: Bagged snacks, milk cartons, cooking oil, etc.
· Consumer goods industry: Boxed shampoo, cosmetics, tissue paper, etc.
· Warehousing and logistics: Connecting production lines or storage areas on different floors, enabling three-dimensional logistics.
· Advantages: Stable goods posture, no tipping; can be designed with multiple levels and in/outlets for flexible diverting/merging; smooth and relatively quiet operation.
3. Screw Elevators (Vertical Screw Conveyors)
· Working Principle: Utilizes rotating helical screws to push material upward within a enclosed housing.
· Suitable Materials: Powdery, granular, and small lump materials without significant stickiness.
Typical Applications:
· Wastewater treatment: Lifting sludge.
· Food industry: Transporting flour, sugar, grains, etc.
· Chemical industry: Transporting certain specific chemicals.
· Advantages: Compact structure, small footprint; completely sealed, dust-free and environmentally friendly. However, lifting height and capacity are limited, and energy consumption is relatively high.
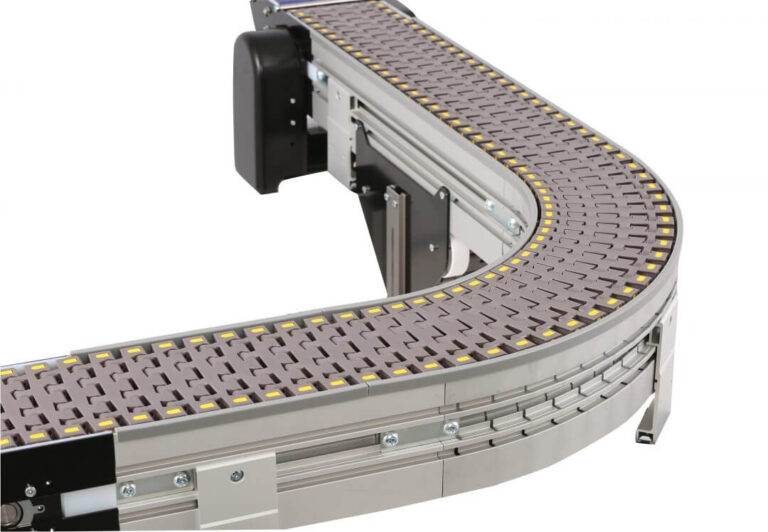
4. Vertical Belt / Chain Plate Elevators
· Working Principle: Goods are placed directly on vertically moving belts or chain plates and are lifted relying on friction.
· Suitable Materials: Unit loads with flat bases, such as bags and boxes.
· Typical Applications: Suitable for light to medium-weight unit load lifting, commonly found in light assembly lines or warehouse interfaces.
5. Hydraulic/Pneumatic Vertical Lifting Platforms
·Working principle: The cargo platform is driven vertically by hydraulic cylinders or cylinders.
·Applicable materials: pallets, heavy goods, and even compatible with forklifts.
Typical application scenarios:
·Production line docking: lifting goods from the ground to the height of the production line, or vice versa.
·Loading and unloading platform: Compensate for the height difference between the truck carriage and the unloading platform.
·Disabled individuals or devices have barrier free access.
·Advantages: Great carrying capacity; Smooth operation; Accurate positioning.
Core Application Value of Lifting Conveyors
1. Space Optimization and Three-Dimensional Utilization:
·Make full use of vertical space to connect production, packaging, and warehousing processes on different floors, reduce floor space, and achieve “space from the air”, especially suitable for cities with high land costs or enterprises with tight internal space in factories.
2. Enabling Automation and Continuity in Production Processes:
· As critical connection points in automated production lines, they ensure seamless and continuous material flow between different processes and equipment, eliminating the inefficiency and interruptions of manual handling. They are cornerstone of building “lights-out factories” and unmanned workshops.
3. Improving Production Efficiency and Reducing Costs:
· Replace a significant amount of repetitive manual handling labor. Lifting speed is much higher than manual, greatly improving logistics efficiency, while reducing labor costs and intensity, and minimizing product damage caused by manual handling.
4. Improving Working Environment and Safety:
· Enable enclosed or semi-enclosed material transport, reducing pollution like dust and noise, thus improving the workshop environment. Also, avoid potential injury risks associated with manual handling of heavy goods.
5. Flexible System Integration and Diverting Function:
· Modern elevators (especially Z/C type) can be designed with multiple inlets and outlets, seamlessly connecting with equipment like roller conveyors, chain conveyors, and sorters. Through PLC control systems, they intelligently transport goods to designated floors and workstations, achieving highly flexible automated logistics sorting and distribution.
Industry Application Examples
· Food and Beverage Industry: From filling, capping, labeling to boxing, palletizing, elevators are needed throughout the process to transport raw materials, empty bottles, and finished cases between different floors and equipment.
· E-commerce Logistics and Express Parcel Sorting Centers: Used for feeding packages into multi-level cross-belt sorters, lifting packages from lower levels to high sorting outlets, or lowering sorted packages to loading areas on different floors.
· Automotive Manufacturing: Lifting components from warehouses to overhead conveyors or assembly lines.
· Pharmaceutical Industry: Lifting raw materials, intermediates, and high-value finished products within clean rooms, requiring equipment that meets GMP standards and is easy to clean.
· Airport Baggage Handling: Lifting checked baggage from check-in counters to underground baggage sorting systems, or lifting sorted baggage to corresponding baggage loading areas.
Summary
Lifting conveyors are indispensable foundational equipment in modern industrial production and logistics systems. Their core application lies in solving vertical material handling problems efficiently, reliably, and automatically. Selecting the appropriate type of elevator (bucket for bulk materials, Z/C for stable unit loads, lifts for heavy loads) and successfully integrating it into the overall material flow can significantly optimize space, improve efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure safety. It is a critical step for enterprises towards intelligent upgrading.